There's No Such Thing As Localized Effects of Birth Control
There's No Such Thing As Localized Effects of Birth Control
I've often heard people repeat from their doctors that the "hormones" in IUD's or birth control in general have localized effects. This seems to imply that the steroid drugs used in birth control formulas go to the reproductive system, do their job of preventing pregnancy, and that's it. Therefore, side effects are considered uncommon.
Well this couldn't be further from the truth. In fact, hormones are known for their taxi-like abilities. Essentially, in order for them to do their jobs, they have to get made in one place and travel to target cells in another place. And that means by definition they get around.
A quick recap - What are hormones?
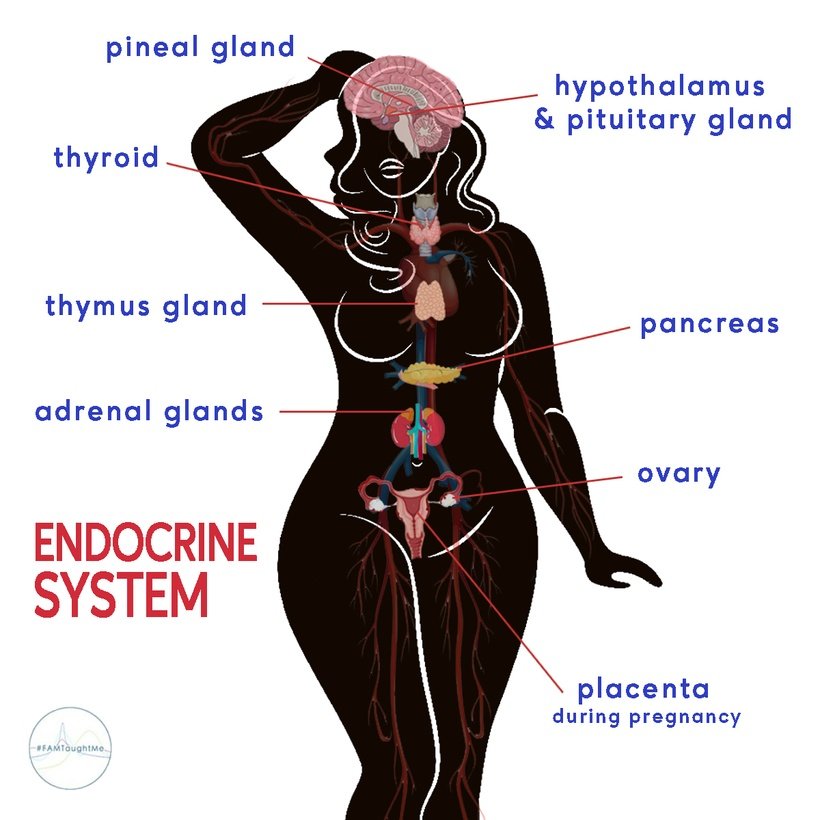
Hormones are chemicals produced in endocrine glands which make up your endocrine system. These hormones are secreted into the bloodstream and travel to different target tissues in other parts of the body. Hormones play a number of complex roles in healthy body development and function.
Some common hormones in the body include:
ADH (anti-diuretic hormone) - Made in the pituitary gland. Is responsible for regulating the balance of fluid and salt in the body. Elevated levels may be caused by the body becoming dehydrated due to sweating.
Adrenaline - Made in the adrenal glands above the kidneys. Responds to situations of danger or stress. Targets many tissues in the body.
Insulin - Made in the pancreas. It plays a vital role in the homeostatic control of blood sugar concentration. The main target tissue for insulin is the liver.
Testosterone - Made by cells in the ovaries. Combined with estrogen, testosterone helps with the growth, maintenance, and repair of reproductive tissues, bone mass, and influences human behavior.
Estrogen - Made in the ovary surrounding the developing egg cell in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. In puberty it causes the development of the female secondary sexual characteristics (breast growth, change in body shape, pubic hair etc.) but in the menstrual cycle, estrogen has a variety of important effects. It stimulates the growth of the endometrium (or uterine lining) to prepare the uterus for the implantation of an embryo. Estrogen also sends messages back to the pituitary gland and can cause the spike in luteinizing hormone (LH) concentrations that trigger ovulation.
Progesterone - Progesterone is also made in the ovary during the post-ovulatory phase, and is secreted by cells in the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine structure that forms after ovulation occurs. Progesterone has two main target tissues: it maintains the thickened lining of the endometrium in the uterus to prepare it for possible implantation. Progesterone also causes the pituitary gland to stop secreting the hormones FSH and LH so a second ovulation/new cycle is never started.
FSH (Follicle-Stimulating Hormone - Made in the pituitary gland in the brain. The target tissues for FSH are the ovaries. FSH is the hormone released at the start of the menstrual cycle that causes one of the immature egg cells in an ovary to begin development.
LH (Luteinizing Hormone) - LH is made in the pituitary gland. It is the hormone that triggers ovulation.
What happens when you take hormonal birth control?
It doesn't matter whether you're taking a combined oral contraceptive (the pill), a progestin only pill, or a hormonal IUD, implant, or ring, the main mode of action is the same: ovulatory suppression.
If there's no egg released, pregnancy is impossible. So let's get into how this actually happens.
Step 1: You consume the pill or insert the product, which causes ethinyl estradiol and/or a progestin of some kind to begin circulating in higher amounts in your bloodstream.
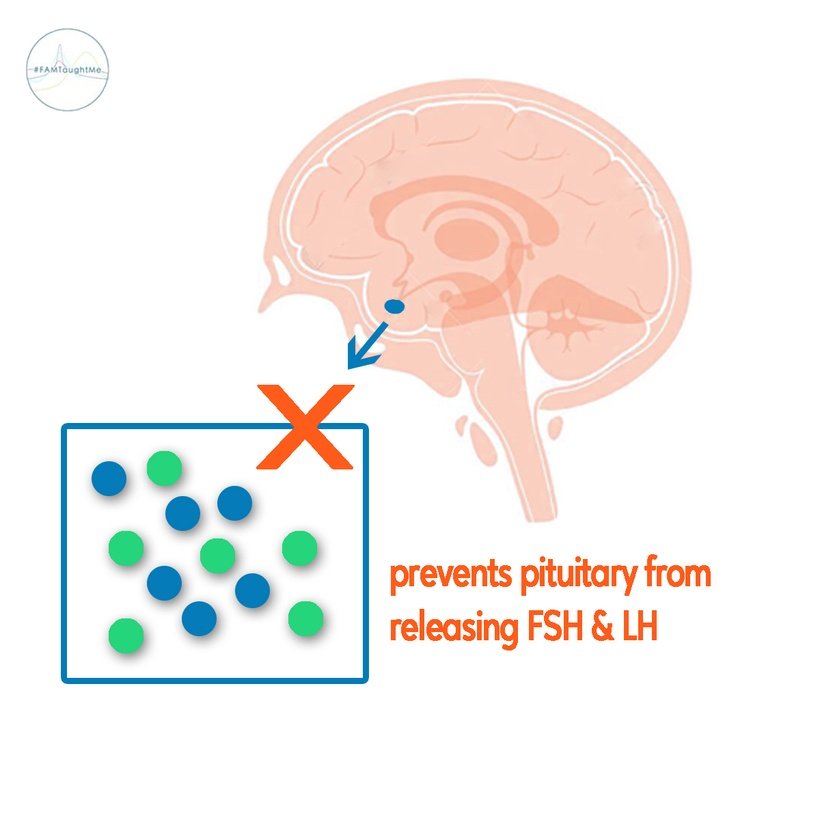
Step 2: A feedback loop sends a message to your brain when there are high amounts of ethinyl estradiol and progestin circulating in your blood to NOT release any more follicle stimulating hormone (develops a new egg) or luteinizing hormone (releases an egg). Your normal ovulatory process is halted and your pituitary stops sending messages to the ovary to start a new menstrual cycle.
Step 3: Ovulation is prevented from occurring. Your hormonal rhythm is plateaued. Remember that birth control is not like pregnancy because during pregnancy your body makes lots of hormones, whereas on birth control your body stops making its natural menstrual cycle hormones.
Step 4: The placebo pills drop the levels of progestin and ethinyl estradiol, and you experience a withdrawal bleed. This is not a menstrual bleed because no ovulation has occurred.
Why the effects of birth control can never be localized.
Hormones made in the body are called endogenous hormones.
Artificial synthesized hormones are called exogenous hormones.
There are MANY cells in the body beyond the reproductive system that contain receptors for estrogen and progesterone. They are virtually everywhere, especially in the brain, affecting how we experience sex, attraction, hunger, eating patterns, stress, and emotions. This allows the hormones to exert effects on a wide variety of tissues. For example there are progesterone receptors in the human heart and cardiovascular system. There are estrogen receptors in the human ear.
Because hormones are signaling molecules, they can be picked up by any cells in the body that have matching hormone receptors. They can easily travel widely through the body via the bloodstream and makes them very efficient communicators. The hormone receptors are programmed to perform different actions depending on whether a hormone is present or not and that has a profound impact on well, YOU.
Although people take hormonal birth control for the targeted effect of preventing pregnancy, or dealing with another reproductive issue, the steroid drugs that mimic hormones are able to trick the hormone receptors, who can't tell the difference. That gives a pretty good rate of effectiveness on the target of preventing pregnancy, but does nothing to stop a wide range of issues that are caused by the drugs binding to *other* sex hormone receptors around the body.
This means that hormonal birth control is affecting billions of cells, and changing their cell processes, in virtually all the systems of the body, including the nervous system, cardiovascular system, skeletal system, immune system, and more.
To make matters worse, the majority of synthetic progestins on the market today are actually synthesized from testosterone. This means that testosterone molecules are adjusted so that they can bind to progesterone receptors, but they don't match up perfectly like true progesterone would to its receptor. This is what is responsible for the pill's sometimes masculinizing effects and contributes to the overall side effects of using the medication.
What are some of the body wide effects of hormonal birth control?
Target Tissue Effect
Heart Increase risk of blood clotting and blood pressure.
Lungs Increase risk of pulmonary embolism. Reduction in maximum oxygen uptake.
Muscles Impairs muscle gains
Liver Liver damage and other related complications such as increase risk of gallstones
Bones Smaller gains or loss of bone mass
The overall effect is that birth control, even if its a "localized" insertion product like an IUD or implant, cannot simply target the reproductive system and only the reproductive system. It targets all different areas of the body because it simply binds to any receptor that will take it.
Questions about hormones and hormonal signaling? Ask me below!